Innovation
- 2025-03-20
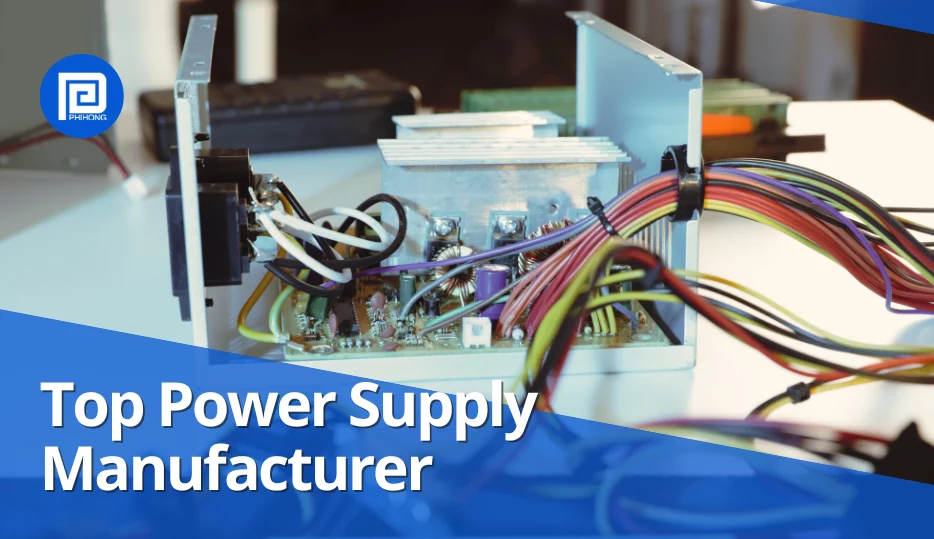
Why Power Supply Matters? A power supply converts electrical energy into the precise voltage and current devices require. It ensures stable performance, prevents damage from power fluctuations, and supports critical features like voltage regulation and filtering. Built-in protection mechanisms enhance reliability and extend the lifespan of electronics, making a high-quality power supply vital for safe … Meet the Top Power Supply Manufacturer – Phihong Read More »
.webp)
- 2025-03-20
Custom power supplies provide tailored solutions for unique performance, size, and efficiency requirements, making them ideal for various applications. At Phihong, we specialize in designing power supplies that meet your device’s specific needs. Manufactured in ISO-certified facilities in Asia, our products adhere to the highest industry standards, including ISO 9001, 9002, ISO 13485, and ISO … Custom Power Supply Solutions for Industrial/Commercial Uses Read More »

- 2025-01-07
Phihong’s compact GaN power supplies are designed for high efficiency and reliable performance across telecommunication, medical, and industrial applications. What is GaN and How Does it Change the Power Supply Industry? Gallium Nitride (GaN) is a revolutionary semiconductor material that’s transforming the power supply industry as it offers significant advantages in terms of … High-Efficiency GaN Power Supply Read More »

- 2024-12-23
Shop Phihong DC industrial power supplies with USA-wide delivery. Get compact, efficient, and durable solutions built for industrial-grade performance. Industrial Power Supply: Reliable Solution for Your Industrial Needs Industrial power supplies are specialized units designed to cater to the rigorous demands of industrial settings. Unlike conventional power supplies, they are engineered to withstand harsh environments, … Industrial Power Supply Read More »
- 2024-11-11
Find out how PoE transmits both data and electric power over a standard cable. Also, see its benefits and common applications in our comprehensive guide. 1. What is PoE – Power over Ethernet and How Does PoE Work? Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a revolutionary technology that transmits both data connection and electric power … What Is Power over Ethernet (PoE)? Benefits, How to Choose & Uses Read More »

- 2024-11-08
Phihong, in collaboration with Vinpower and Silanna Semiconductor, has developed the iXCharger 65W, which has been honored with an Innovation Award during the 2024 CES (Consumer Electronics Show). This first of its kind, two-in-one charger + storage device not only boasts an impressive storage capacity of up to 1.5TB, but also combines an efficient 65W … Phihong and Vinpower Collaborate to Create the ‘iXCharger 65W’ GaN Charger + Storage, Honored with a 2024 CES Innovation Award! Read More »

- 2024-11-08
Phihong Technology has once again pushed the boundaries of industry standards by launching its new 330W GaN power adapter for gaming laptops. Featuring third-generation Gallium Nitride (GaN) technology, it achieves a power density of 14.5 W/in³ (1W/cc), nearly 50% smaller than other products with similar power output, and weighs under 800 grams. This product meets … Phihong Introduces 330W Ultra-Light GaN Gaming Laptop Power Adapter, Setting New Power Density Standard Read More »

- 2024-11-07
Phihong Technology launched a new 280W GaN (Gallium nitride) power for high-power gaming laptops at the end of 2021. The 280W GaN gaming power supply highlights a performance level that leads the industry in an ultra-compact case size of 160mm x 69mm x 25mm (276 cc) and a 700g lightweight design. At 16W/in3 power density, the … Phihong launches a 280W GaN Charger suitable for gaming laptop Read More »